grid-layout-plus是一个支持拖动、重新设置大小的网格布局组件。它的代码是在vue-grid-layout的基础上修改的,而 vue-grid-layout 又是参考 gridster.js 和 react-grid-layout。我们这里之所以讲 grid-layout-plus 是因为 grid-layout-plus 是基于 vue3 的,而 vue-grid-layout 是基于 vue2 的,当然组件的核心思想都是类似的,看懂一个组件其他的也会明白。
基本使用
我们这里直接用 grid-layout-plus 的官网示例来演示,代码如下:
1 | <template> |
布局 Layout 的类型定义如下,它是由 LayoutItem 的数组组成,而 LayoutItem 的必须字段有 w、h、x、y、i,分别表示 宽、高、X坐标、Y坐标 和 索引(id)。grid-layout-plus 默认把一行分为 col-num (默认 12)个元素份,每份高度row-height (默认 150 像素),而 w、h、x、y 传的值是占据了多少份,而不是像素。
1 | export interface LayoutItemRequired { |
此时的效果可以点这里。
组件结构
grid-layout-plus 的核心组件就2个 grid-layout 和 grid-item。grid-layout是一个容器,用来计算网格布局;grid-item是拖动组件,内部使用 interact.js 来实现拖动和调整大小。
grid-layout 的基础结构如下:
1 | <script setup lang="ts"> |
从上可以看到,如果没有默认插槽的话,grid-layout-plus 会使用 GridItem 组件来渲染布局。此外在 idDragging 的时候会渲染 placeholder 。
grid-item 的基础结构如下:
1 | <script setup lang="ts"> |
由上可见,grid-item 组件调用 tryMakeDraggable 和 tryMakeResizable 函数通过 interact.js 来分别实现拖动和调整大小的功能。
组件通信
grid-layout 与 grid-item 数据通信部分是通过 props 来实现的,这一点可以在上述 grid-layout 组件中 #item 插槽中的 v-bind="item" 来知晓。还有一部分通信方式是通过 inject 来实现的,代码如下。
1 | // src\helpers\common.ts |
grid-layout 把自己的 props 和 state 以及 emitter 提供给 grid-item 组件使用。通过 inject 方式不但可以直接获取到 grid-layout 的所有状态,还可以拿 emitter 来触发的事件,哪怕 grid-layout 和 grid-item 隔了好几个组件,依然可以正常运行。
我们以 setDraggable 事件为例来讲解,当 grid-layout 的 props.isDraggable 发生变化时,grid-layout 会通过 emitter 触发 setDraggable 事件,grid-item 组件监听 setDraggable 事件,调用 setDraggableHandler 函数来处理。这里 grid-item 首先会判断 props.isDraggable ,如果为空的话则根据 grid-layout 的 props.isDraggable 来判断是否可以拖动。也就是说自己组件的 props 的优先级大于 grid-layout 的 props,这就可以保证 grid-item 在拖动上做到个性化,即使 grid-layout 不支持拖动,也可以自己设置 props.isDraggable 来支持单个 grid-item 拖动。
上述 increaseItem 和 decreaseItem 是在 grid-item 把自己的实例添加到 grid-layout 中了,这样 grid-layout 暴露给外界的 getItem 方法就可以获取到子组件中的信息了,不过这里本章无需关注。
grid-item 处理 resize 和 drag
在 grid-item 中,tryMakeResizable 方法,通过 interact.js 的回调函数调用 handleResize 函数来处理调整大小的逻辑。
1 | let innerX = props.x |
handleResize 通过 state.resizing 对象来保存 resize 过程中当前 grid-item 的宽高, state.isResizing 来记录是否处于移动过程中,这两个值后面还会用到。然后通过新的宽高计算出新的 w 和 h(份数), 当然把它们限制在最小和最大范围内,最小是 1。最后通过 props 暴露 resize 和 resized 事件,再通过 emitter 触发 resizeEvent 事件,告诉 grid-layout 组件当前 grid-item 的大小已经改变了。
handleDrag 的处理与 handleResize 类型,只不过 handleResize 修改的是 grid-item 的宽高,而 handleDrag 修改的是grid-item 的位置,具体代码如下:
1 | function handleDrag(event: MouseEvent) { |
handleDrag 中通过 state.dragging 记录位置信息(top 和 left),当然这里还支持 rtl。最后通过 emitter 触发 dragEvent 事件,告诉 grid-layout 组件当前 grid-item 的移动了。
综上,handleResize 和 handleDrag 就是计算出新的宽高或位置,并告诉 grid-layout 变化信息。
grid-layout 处理 resize 和 drag
当 grid-item 宽高或者位置变化的时候,就会影响到其他 grid-item 位置的变化,这里就需要在 grid-layout 处理其他grid-item 的位置信息。
1 | // src\components\grid-layout.vue |
在 grid-layout 中最重要的两个函数就是 resizeEvent 和 dragEvent 函数。我们先看 resizeEvent。
1 | function resizeEvent( |
resizeEvent 的主要功能有修改 placeholder 的宽高和位置和显示,当设置 state.isDragging = true 的时候则显示 placeholder (可以在上面 组件结构 中看到相关代码);如果设置了 responsive 则处理响应式布局;然后收缩布局并触发事件。compact 方法是 grid-layout 的核心算法,稍后我们再讲。触发 emitter.emit('compact') 则通知 grid-item 重新渲染。这个流程起初是在 grid-item 通知到 grid-layout 现在又回到 grid-item 了,当然这里通知的是所有的 grid-item 。
dragEvent 与 resizeEvent 的代码也是大同小异。
1 | function dragEvent( |
dragEvent 与 resizeEvent 最大的不同是调用了 moveElement 方法。resize 的时候影响的是当前 grit-item 的宽高,同时会影响右侧和下方的元素 y 值变化,这个过程的逻辑在 compact 函数里面,作用是消除空白区域使其紧凑。但是 drag 的时候修改的是位置,位置一变化,甚至会导致上面的元素挪到当前移动元素的下方,也就是换位,这就有了 moveElement 方法。
1 | /** |
在 moveElement 中,对当前元素的移动通过给 x 和 y 坐标赋值来实现。然后遍历所有碰撞的元素,来做级联移动。在 moveElementAwayFromCollision 中第二个参数是碰撞的不动的元素,第三个参数是要移动的参数,如果 collision.static 为 true 的时候,则collision不动,移动当前元素;否则当前元素不动,移动碰撞的元素,这里很巧妙地通过参数的位置就实现了静态碰撞元素的处理。
1 | /** |
moveElementAwayFromCollision 中如果是用户手动操作,则把目标移动到 collidesWith.y - itemToMove.h 位置,这样目标与 collidesWith 刚好不碰撞。当然需要调用 getFirstCollision 检测一下,没碰撞就移动到这个位置,如果碰撞了则往下移动一格。之后调用 moveElement ,由于碰撞的 item 向下移动了一格,又会引发它下面的项目级联移动,直到所有元素都没发生碰撞。
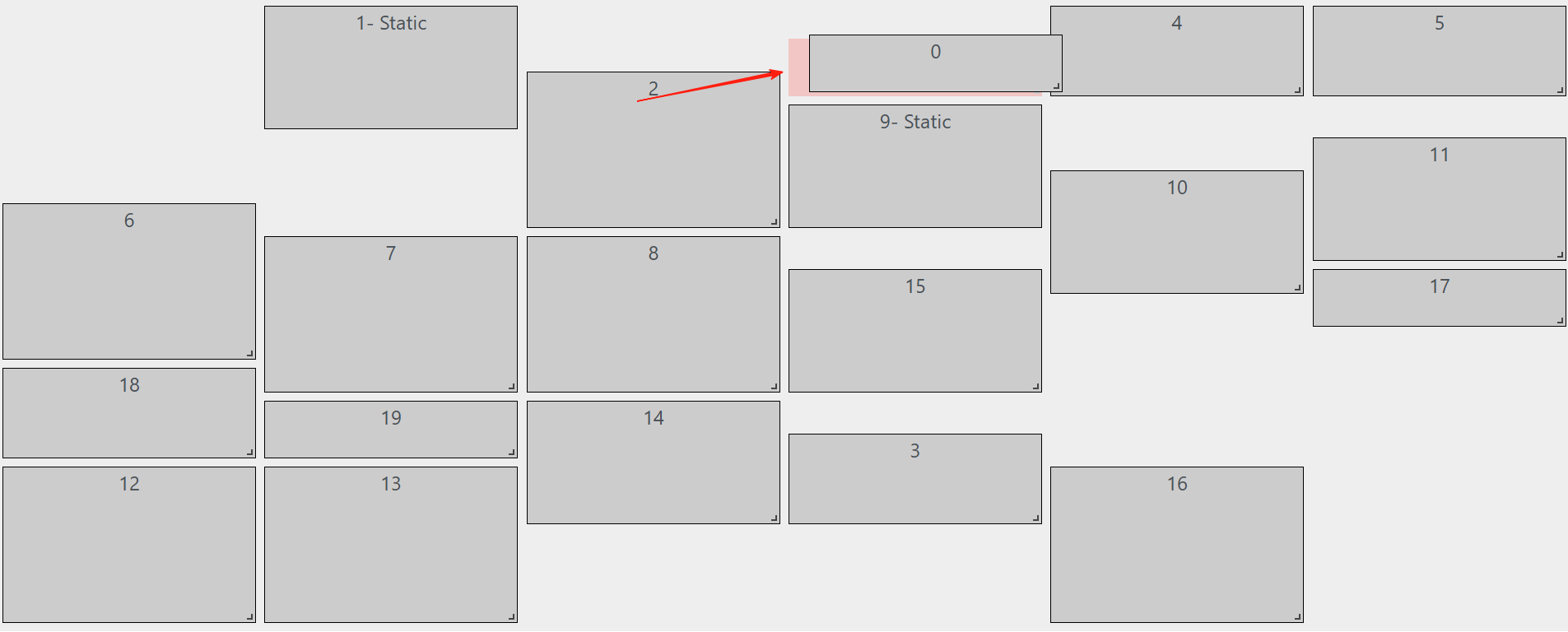
如果对移动到 collidesWith.y - itemToMove.h 位置不理解,可以看下图,0 放在某个静态块的上面,如果 vertical-compact 的 props 为 false 时,就应该刚好放在静态块的上面;当然如果为 true 则后面的 compact 函数会把它处理在最顶部。
compact 实现
compact 方法是使得所有元素变得紧凑。在介绍 compact 前先看几个辅助方法:
1 | /** |
这些方法整体比较简单,我们再看 compact 方法:
1 | /** |
compact 先获取所有静态的元素赋值给 compareWith 。然后排序,以保证遍历的顺序是从左往右,从上到下的。然后对排好序的元素进行遍历。对于非静态的处理后加入到 compareWith 中(静态的已经在里面了)。这样就可以先确认静态元素的位置,然后从左到右从上到下把没碰撞的元素加入进来。
把元素处理成没碰撞的位置代码如下:
1 | /** |
compactItem 中,verticalCompact 为 true 的时候,则需要变的紧凑,变紧凑的过程是先把元素往上移动,移动到第一个发生碰撞的地方。当然如果一个元素上面是静态元素,那么向上移动肯定会碰撞的,所以向上移动后对于发生碰撞的元素还需要向下移动,直到不碰撞位置。这样在 compact 中遍历完所有排好序的元素,就会使所有元素变得紧凑。
grid-item 处理 compact 事件
还记得 grid-layout 无论是 dragEvent 还是 resizeEvent 在调用完 compact 方法都会调用 emitter.emit('compact') 吗?这是触发所有 grid-item 元素的 compact 事件,grid-item 中处理如下:
1 | emitter.on('compact', compactHandler) |
在 createStyle 中先让 innerX 和 innerW 设置在一个合法的数值范围内,然后获取到位置信息 pos, 还记得之前的 state.dragging 和 state.resizing 吗?如果处于 drag / resize 过程中,则把对应的坐标给 pos。然后通过 useCssTransforms 来判断是使用 transform 还是 top/left 来设置位置。最后修改 state.style,在模版中对应的 grid-item 的 style 就会改变。
这就是 grid-layout-plus的核心流程,还有一些响应式等逻辑没有介绍,相信你也能看得懂对应的源码。